Difference between Overweight and Obese
What are obesity and overweight?
- Obesity: is a long-term medical problem where extra body fat has built up to the point where it could be harmful to one’s health.
- Overweight: is a condition in which a person’s body weight is greater than what is considered healthy for their height.
Both obesity and overweight are defined using body mass index (BMI), a measure of body fat based on height and weight.
- Obesity is a BMI of 30 or higher.
- Overweight is a BMI of 25 to less than 30.
A person with a BMI of 25 to less than 30 is considered to be overweight. This means that they have more body fat than is considered healthy. A person with a BMI of 30 or higher is considered to be obese. This means that they have a much higher amount of body fat than is considered healthy.
Being overweight or obese carries a number of health hazards. These include heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis.
It is crucial to remember that BMI is not a precise indicator of body fat. It does not account for things like bone density and muscle mass. Therefore, a person with a high BMI may not actually be obese, and a person with a low BMI may actually be overweight.
If you are concerned about your weight, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you determine your BMI and discuss your individual health risks. They can also help you develop a healthy weight loss plan.
Health Risks of Overweight and Obesity
Heart disease: Excess weight can put extra strain on your heart and blood vessels, increasing your risk of heart disease.
Stroke: Obesity is a major risk factor for stroke, which is a serious condition that can cause brain damage or death.
Type 2 diabetes: People who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition that affects how your body uses sugar.
Certain types of cancer: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including breast cancer, colon cancer, and endometrial cancer.
Osteoarthritis: Excess weight can put extra stress on your joints, increasing your risk of osteoarthritis, a painful joint condition.
Sleep apnea: Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that occurs when your breathing stops or becomes shallow during sleep. People who are overweight or obese are more likely to experience it.
Fatty liver disease: When your liver becomes fatty, you have fatty liver disease. It is more common in people who are overweight or obese.
Mental health problems: People who are overweight or obese are more likely to experience mental health problems, such as depression and anxiety.

What is BMI?
A measurement of body fat is the body mass index (BMI), which is based on height and weight. By dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared, the BMI is determined.
BMI is a useful tool for assessing weight status in adults. However, it is important to note that BMI does not take into account factors such as muscle mass and bone density. Therefore, a person with a high BMI may not actually be obese, and a person with a low BMI may actually be overweight.
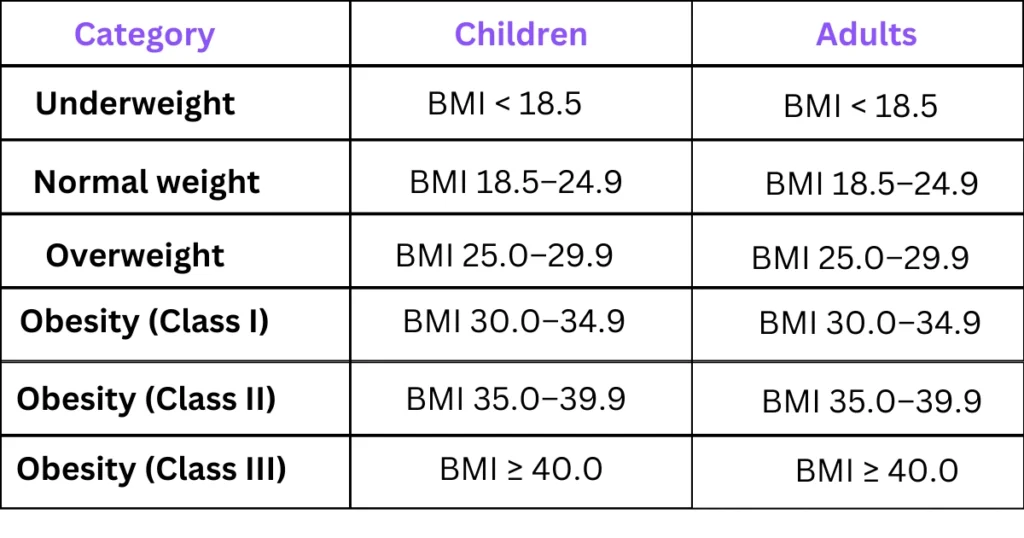
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines the following BMI categories:
Underweight: BMI < 18.5
Normal weight: BMI 18.5–24.9
Overweight: BMI 25.0–29.9
Obesity (Class I): BMI 30.0–34.9
Obesity (Class II): BMI 35.0–39.9
Obesity (Class III): BMI ≥ 40.0
Calculating BMI
The formula for BMI is:
BMI = weight in kilograms / height in meters squared
For example, if you weigh 70 kilograms and are 1.7 meters tall, your BMI would be:
BMI = 70 kg / (1.7 m)^2 = 24.2
Comparison chart for both children & Adult
What causes excess weight?
Genetics: Genetics plays a role in determining how easily a person gains weight. Some people are more genetically predisposed to gaining weight than others.
Environment: The environment in which we live can also influence our weight. For example, people who live in areas with more fast-food restaurants and fewer grocery stores are more likely to be overweight or obese.
Diet: The foods we eat can have a big impact on our weight. Eating too many calories, especially from unhealthy sources like processed foods and sugary drinks, can lead to weight gain.
Physical activity: Physical activity helps us burn calories and stay at a healthy weight. Overweight or obese individuals are more prone to be physically inactive.
Stress: Stress can also lead to weight gain. When we are stressed, our bodies release hormones that can lead to increased appetite and decreased metabolism.
Certain medications: As a side effect, several drugs can make you gain weight.
Medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism, can also lead to weight gain.
The consequences that obesity brings to human health
- increased risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and several cancers.
- Increased risk of sleep apnea, fatty liver disease, and orthopaedic problems.
- Increased risk of social and emotional problems.
- Shortened lifespan.
Conclusion
Obesity is a serious health condition that can have a number of negative consequences for your physical and mental health. If you are worried about your weight, it’s crucial to talk to your doctor. They can help you determine if you are overweight or obese and discuss the best way to manage your weight.
